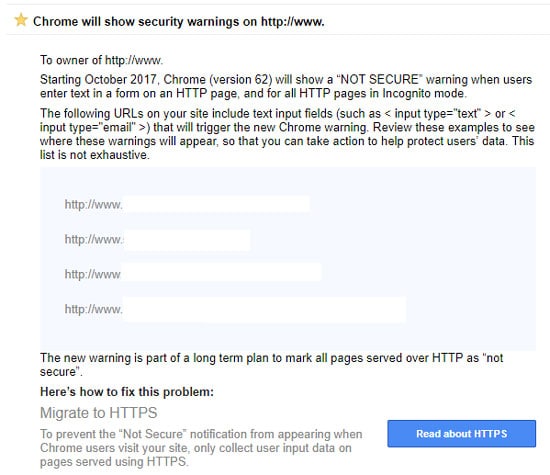
Google has sent out a string of warnings to website owners and users with a Google Search Console account about the Google HTTPS Chrome security alerts. The warning states that Chrome will show security warnings on your site if a user enters text into a form on an HTTP page and also for users using incognito mode on an http page. This is for all users with a Chrome browser. Below is an example of the https security warning from Google.
Google HTTPS
It has been a long time coming with Google switching to an https protocol. The internet has been moving to a much more secure ecosystem and this is Google’s way of pushing it’s agenda. If your site is not https:// secure, then your rankings will most likely decline over time.
Even the Certification Authority Authorization (CAA) DNS Resource Record was proposed to strengthen the public key infrastructure (PKI) for websites with digital certificates by September 2017. This allows a public Certification Authority to implement additional controls to reduce the risk of unintended certificate mis-issue. Here’s more information on the HTTPS CAA improvements for websites.
Migrating to a Secure Site
If you want to retain your ranking on your website, you should highly consider migrating to an HTTPS secure site. You can read more about securing your site with HTTPS and understand the best practices to moving to HTTPS. Make sure you pay special attention to the server-side 301 redirect recommendation. This is where most people will wreck their site with organic search traffic with 404 errors and bad 301 redirects. This is where Google is not kind to a website making the HTTPS switch with organic traffic and rankings slipping quickly over a few days.
How a Secure HTTPS Connection Works
![]()
HTTPS process of how a secure transport link is completed between a website visitor (client) and your server:
- The website visitor makes an HTTPS request to your server.
- Your server will send over a copy of its SSL certificate and a copy of its public or private key back to the website visitor.
- The website visitor will then verify the identity of your server with the Certification Authority (CA) to create a secure connection with your server. A secret session key is then generated from the website visitor (client) and the data is encrypted.
- Your server will then decrypt the secret session data (with the public or private key) and verifies the connection has been made.
- Now we have a fully secure HTTPS connection between your server and the website visitor (client). All messages, private information, credit cards, etc. can be sent back and forth securely.
We have our own SEO checklist with switching from HTTP to HTTPS to ensure there is minimal impact with SEO, PPC and other traffic sources. Check every URL on both HTTP and HTTPS and make sure everything is working properly. Once your site is completely switched to HTTPS, use the Qualys SSL Server Test tool (free online) to verify your site is secure.


